Basic Searching
Most searches can be conducted through the Search bar at the top of the page. By typing in multiple words or a phrase, the results will return where any of the words entered is found, e.g. searching Queen's University will return anything with Queen's or University (or both) in the description.
To search by a specific phrase, use quotation marks ("") around the phrase, e.g. "City of Kingston". Boolean search logic can be applied to any search term to include or omit certain words or phrases from your results. This includes:
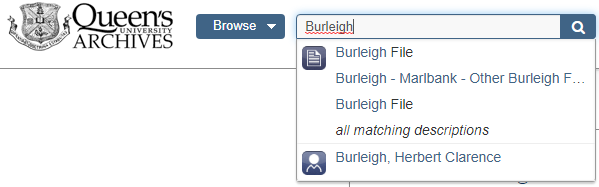
When you start to type a search term, a short list of predictive terms will appear below. You may click on any one of the terms should it match what you are seeking.
Search results
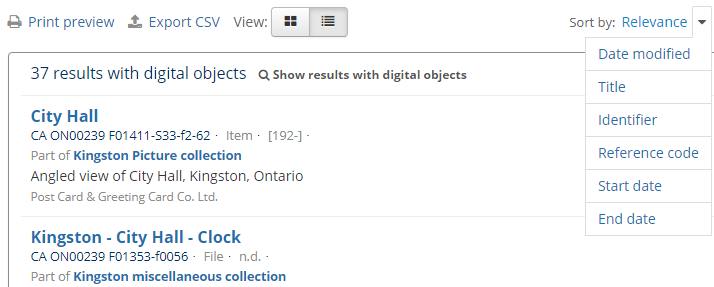
Search results are sorted by relevance to your search term(s), and will include all levels of description. To change the sort order of your results, click on the drop-down menu to the right of the search results.
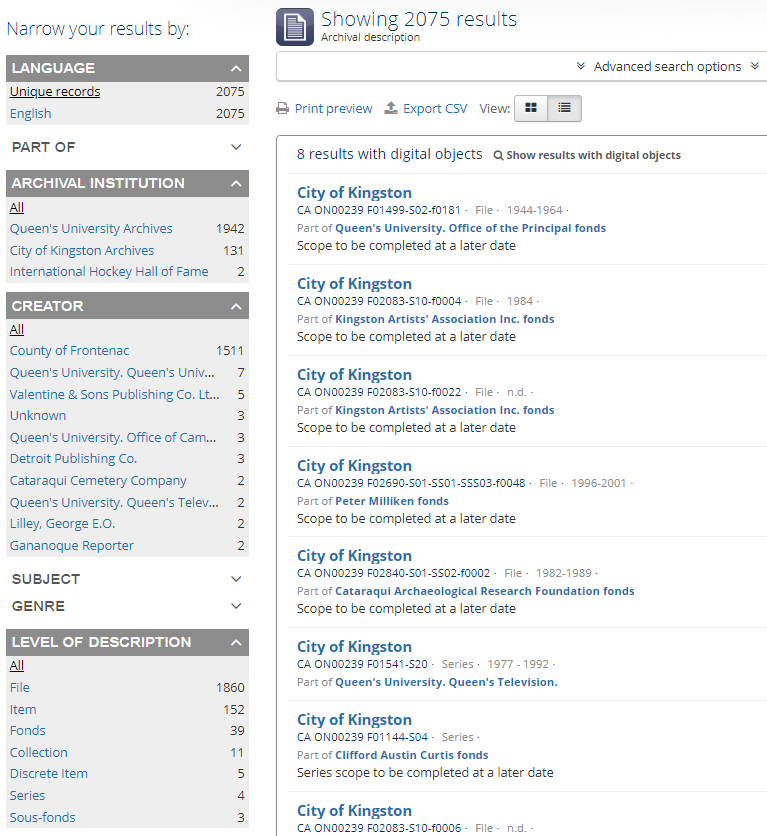
To further narrow or filter your search results, terms are available at the left side of the page beside the results list. Options to narrow your search include filtering by the most popular fonds or collection containing your search term (Part of), Institution, Creator, or Level of Description. Limiting your search results to Level of Description, for example, will return only the uppermost level of description by selecting Fonds or Collection.
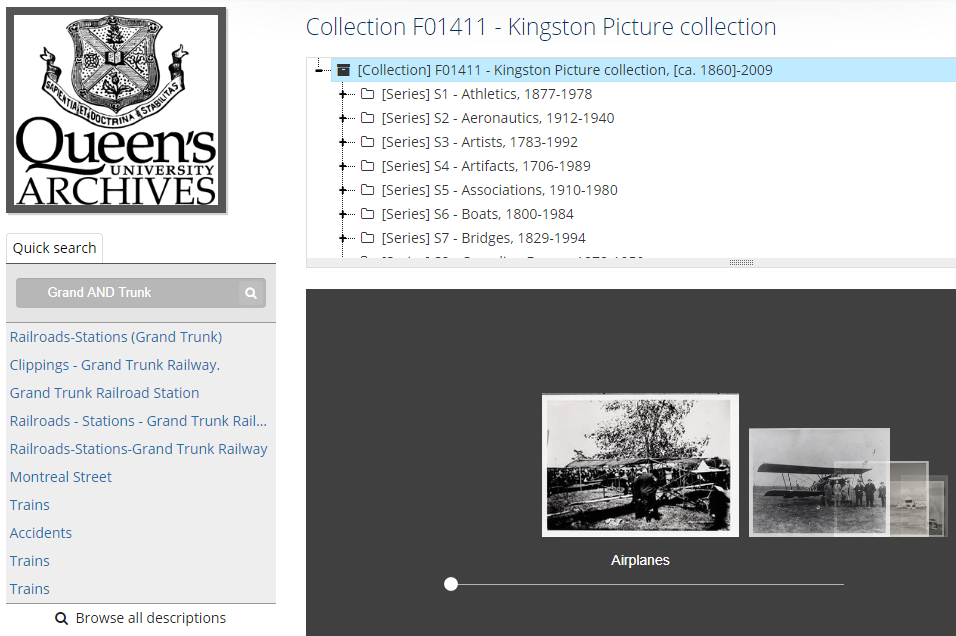
Search within an Upper-level description (Quick search)
By navigating to a fonds- or collection-level description, a Quick search box will appear on the left side under the institution logo. Using the same search logic indicated in Basic Searches, you can find descriptions within that particular fonds or collection.
Click one of the results to view the complete record. The tree view above the description will illustrate where the file is located within the fonds or collection.
Advanced Search
Search results can be further pared down by using filters under Advanced Search. Filter options include:
Advanced search logic
| Symbol | Use |
|---|---|
| “ | Term enclosed in quotes must appear exactly as provided. Example: “towel” will find towel, but not towels. |
| + | Term after “+” must be in the result. Example: +tea cricket requires that results that must contain the term tea in them, and may have the term cricket. |
| - | Term after “-” must not be in the result. Example: -tea cricket requires that results that must not contain the term tea in them, and may have the term cricket. |
| ? | Single character wildcard. Example: p?per will find paper and piper, but not pepper. |
| * | Multiple character wildcard. Example: galax* will find galaxy and galaxies, but not galactic. |
| ~ | Fuzzy search. Will return results with words similar to the term. Example: fjord~ will find fjord, fjords, ford, form, fonds, etc. |
| && | Boolean operator. Can be used in place of AND. Will cause an error if combined with spelled-out operators. Example: Arthur && Ford AND Zaphod will fail; Arthur && Ford && Zaphod will succeed. |
| ! | Boolean operator. Can be used in place of NOT. Will cause an error if combined with spelled-out operators. |
| ^ | Boost relevance. Multiplies the relevance of the preceding term by the number following the symbol, affecting the sorting of the search results. Example: paranoid android^5 gives results containing the term “android” 5x the relevance as results containing only the word “paranoid”, and will sort them closer to the start of the search results. |
\ | Escapes the immediately following character, so that it is treated as text, rather than as a special character. For Example, to search for “(1+1):2”, use the following: \(1\+1\)\:2
|
| ( ) | Used to group search clauses. This can be useful if you want to control the precedence of boolean operators for a query, e.g. (coffee NOT tea) OR cream will return different results than coffee NOT (tea OR cream). Without grouping, by default in Elasticsearch, NOT takes precedence over AND, which takes precedence over OR. |
| [ ] | Closed interval range search. Example: [“Frogstar” TO “Magrathea”] will return results in the alphabetic range between “Frogstar” and “Magrathea”, including”Frogstar” and “Magrathea”. |
| { } | Open interval range search. Example: {“Frogstar” TO “Magrathea”} will return all results in the alphabetic range between “Frogstar” and “Magrathea”, excluding”Frogstar” and “Magrathea”. |
For further advanced search tips, you can also visit https://www.accesstomemory.org/en/docs/2.5/user-manual/access-content/search-atom/#search-atom
Requesting a File or Item
The easiest way to request multiple files or items is by using the Clipboard feature. Upon navigating to the file- or item-level description, click the Add button under the Location box. This will save the description to the clipboard.
Once you have selected the files and items, click on the Clipboard icon () in the upper-right corner and "Go to clipboard."
From here, Save your clipboard and note the ID - you can pass this along to the archivist in person or by email to request the list of files.
